Email validation is a process that helps you identify invalid emails and email bounces, keeping your subscription lists clean. Let’s see how you can avoid spam traps from damaging your sender reputation because not every email address you capture is a keeper.
Email validation for marketers who send high-volume email campaigns is not a recommendation. It’s a must.
It’s a something you must create and follow-through regularly in your email hygiene routine to make sure that you’re sending your messages to valid, active, even engaged email addresses. Your sender reputation, email deliverability, and the effectiveness of your email marketing campaigns depend on it.
Unfortunately, you can’t always depend on the individuals who fill out your sign-up forms to provide you with an email address that meets these criteria. For example, someone could enter an incorrect email address accidentally. Alternatively, a person or a bot might intentionally enter a fake or malicious email address.
Regardless of the reason, you need to prevent invalid email addresses from corrupting your subscriber lists. That’s where email validation comes in.
Using an email validation tool, you can identify and eliminate invalid email addresses before sending them a message. This helps avoid those unpleasant and totally avoidable hard bounces.
Of course, there are hard bounces from other sources (more about that later).
How does it work?
That’s where this article comes in.
Keep reading to learn how email validation helps keep your lists clean and your reputation safe.
Intro into information validation: how it all started

For as long as people have shared information, some of that information has been false. Sometimes people didn’t have all the facts, or the information they had was inaccurate. Other times, honesty and accuracy weren’t high priorities for the people sharing the information.
For example, during the first half of the 20th century, news publishers’ priority was selling magazines and papers–the more, the better. Publishers adopted an attitude of “Give the people what they want” and used emotion-driven headlines and sensational stories to boost sales and increase circulation.
Given the limits of long-distance communication at the time and the heightened emotions triggered by two world wars, it wasn’t difficult for enterprising publications to find creative ways to stimulate people’s emotions.
Journalists desperate to win a position on the front page sometimes found a little embellishment could take them a long way. It was clickbait without the clicks.
But, the flood of misinformation eventually led to a backlash of media mistrust.
“Fake news! Yellow journalism! You can’t trust the media!”
One publisher, Time Magazine, saw this credibility gap as an opportunity–to do better. The magazine committed to begin fact-checking every fact in each of its articles before publishing them.
Led by Nancy Ford, the Time Magazine’s fact-checking team dug into the details of every story to ensure that the magazine’s articles were accurate. This effort earned the publication a reputation for reliability and integrity.
The journalistic standards set in motion by Time Magazine still exist today, and media watchers are eager to point the finger at publishers who fail to check their facts.
Modern publishers must pay attention to the accuracy of their stories or risk their brand’s reputation.
Checking your facts is important for email marketers, too.
While the general public may not be watching to see how well you check your subscriber lists, internet service providers (ISPs) and Simple Mail Transfer Protocol servers (SMTPs) are.
Sending an email to a list of subscribers without first confirming the accuracy of that list puts your brand at risk.
When you send emails to non-existent or invalid addresses:
- Your message isn’t reaching your audience.
- The resulting bounces will draw reputation-damaging attention from ISPs and SMTPs.
- You may be messaging a spam trap (also known as honeypots) and end up on a blocked sender list.
Email validation protects you from these hazards by identifying invalid or fake email addresses before you send them a message and allows you to focus your resources on real, active email recipients.
What exactly is email validation, and how does it work?
You’ll find the answers in the following selections, as well as tips for using email validation and verification services to protect your reputation and improve your campaign performance.
What does email validation validate?
Even the best marketing campaign can’t succeed without an audience. For email marketers, that audience is people associated with the email addresses on their subscriber lists.
The success of your campaigns hinges on the quality of your lists. Controlling that quality begins at the point of capture. Are you collecting genuine, usable email addresses?
Email validation helps you figure that out.
Email validation is the process of determining whether an entry in your sign-up form or database’s email field is a valid email address.
A basic email validation check will confirm that the email address conforms to the necessary formatting (syntax) rules to be an email. Email validation may also confirm that an email mailbox matching a particular address is registered with the receiving domain.
There are other validation and verification checks that go beyond the basics.
Additional tests and checks help you ensure that the email addresses you capture are not only functionally accurate but are attached to real, credible email accounts. Other checks take existing email addresses, checking if they’re still valid after they’ve been on your email list for a while.
There’s a rule of thumb in email marketing. You can expect about 30% of your email addresses to churn every year for various reasons, and that’s a problem you must deal with head-on.
There are several ways to deal with this issue, but automating this process is the best way to go about it, either by developing something or using an email validation service.
Using an email validation service
If you are capturing thousands of emails daily, you know already that running a validation check of each email you receive is impossible. You can often save time and achieve greater efficiency by outsourcing this task to a dedicated email validation service provider.
These services automate and streamline the process of checking emails individually and in bulk. Some can turn around results for thousands of addresses in just a few minutes.
When can you validate an email?
You can use an email validation service to review emails in real-time while an address is entered into your form or database. You can also choose to collect these emails and validate them in batches.
You may have experienced real-time email validation when you shop online, filled out sign-up forms to access gated content, or subscribe to newsletters.
Real-time email validation
Scrubbers usually check the email and immediately alert the person entering the data that there
is an error so they can correct it. The chances of you receiving a message depend on which tests the brand has chosen to employ.
A basic real-time test would kick back an email if you made a syntax error, such as putting a period at the end of your address. A more sophisticated filter might refuse to accept non-business email addresses such as those using Gmail or similar services.
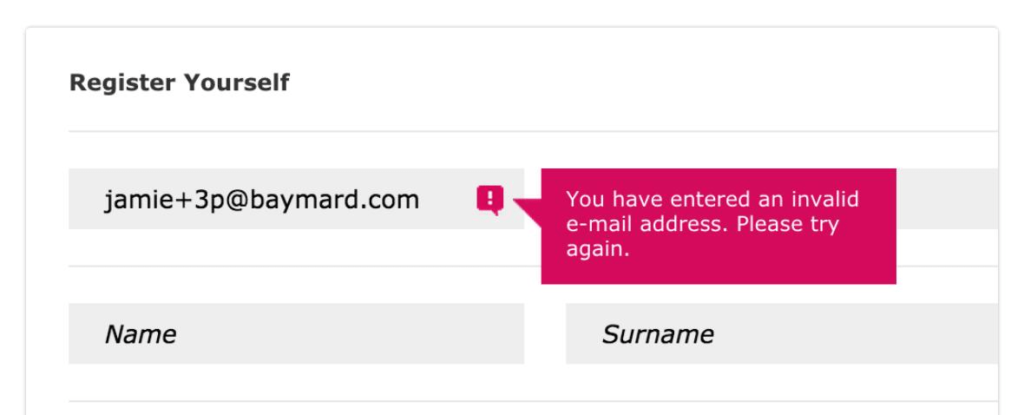
These in-the-moment validation checks add a little friction to your sign-up process but can help you capture more legitimate addresses by preventing user errors. Adding more restrictions on what type of emails you’ll accept increases the friction. But, it can also increase the quality of the emails you capture.
Batch or bulk validation
These services enable you to check a collection of newly captured addresses by uploading a large file to your validation service provider. You can also use bulk validation to review all or a segment of your existing subscriber list. If your bounce rates are above 2%, it might be a good idea to validate the affected segments as part of your “what’s going on!” investigation.
This bulk validation report from Mailgun by Pathwire can be downloaded as a CSV or JSON file and summarizes the results. Notice that Mailgun uses categories for valid and invalid emails as well as catch-all, unknowns, and high-risk addresses (“do not send”) in its report.
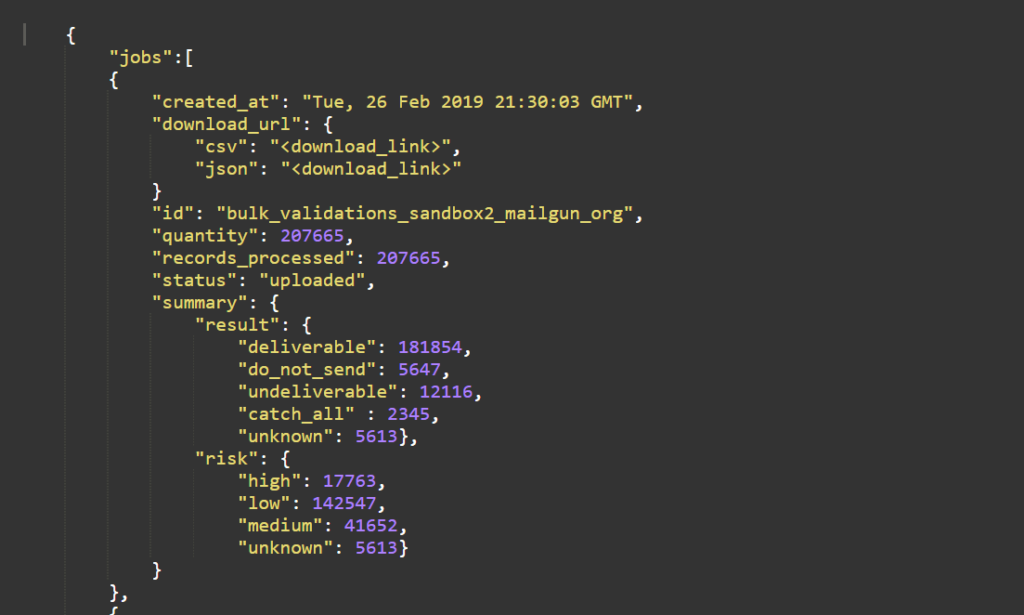
Bulk validation is useful for screening your active subscriber list to identify addresses that may have been valid when you added them to your list but are no longer active and may have been converted to spam traps.
When you validate new address submissions, don’t allow them onto your active subscriber list until this step is complete. Until then, keep them in a separate, quarantined database. If you’re validating an active list, be sure to have a protocol for removing any problem emails your service identifies.
The difference between email validation, verification, and list hygiene services
When you request an email check, most email validation services will provide you with a report indicating one of the following statuses:
- Valid. Depending on the provider, this status may mean that the email has been verified and it exists or that the email exists, is active and accepting mail.
- Invalid. This means that although your email validation provider verified this email, it doesn’t exist. It’s inactive or is not accepting mail. Included in this category would be entries that fail to meet the functional standards to perform as an email.
- Unknown. If an email address status can be determined, it falls under this category.
This category includes emails that didn’t make it all the way through the validation process. Sometimes this happens when an SMTP server accepts all emails sent to its domain, whether they have an associated account or not.
- Do not send. Some email validation providers maintain a separate category for emails that are valid but bad news for senders.
These may be email addresses that have a reputation for making spam complaints or are associated with problematic domains.
Some services may include additional checks and list hygiene tasks. These providers, often called verification or list hygiene services, generate granular results with value and risk-related details about each email address that go beyond the basic categories.
How is email verification different from validation?
Email verification goes beyond confirming that an address is “functionally valid and exists.” Verification services use public and/or proprietary data to determine if an account is active and connected with a real person. This helps keep unengaged subscribers and spam traps off your lists.
The more in-depth a verification process is, the more information the service provider can offer you about your subscribers.
A report from a verification service may include some or all of the following status categories:
- Duplicate. A list hygiene service will compare the emails you’ve submitted for review to your existing list and alert you to any duplicate addresses.
- Catch-all. Catch-alls accounts catch emails sent to a valid domain but not to an existing address. A corporation might use a catch-all address to make sure they capture everything sent to their domain. However, no one person is reading those messages.
- Role-based. are email addresses not owned by an individual but used by a company to gather general messages (e.g., info@mycompanysdomain.com or sales@thisdomain.com)
These addresses are considered low-value because they aren’t reaching a person likely to respond to your message.
- Free email domain. Not every holder of a free email account is the wrong type of lead. However, some B2B marketers prefer to limit their lists to addresses from other business domains.
- Random or auto-generated address. An address consisting of a random string of characters is more likely to be a throwaway or fake account or associated with a bot than a readable one. Some services will flag addresses that appear auto-generated even if associated with a legitimate domain.
- Disposable or temporary. Disposable email addresses (DEAs) or burner addresses are email addresses that expire after a short period. Once the address expires, messages sent to them will bounce.
Some DEAs are recognizable because they use a domain associated with a temporary mailbox provider. Others can be harder to detect.
- Alias or forwarding address. Consumers who don’t want to reveal their primary email can create an alias address and connect it to their main account. Messages sent to the alias address are quarantined in a folder separate from the recipient’s regular emails.
Alternatively, email users can create a separate email account and then forward its messages to their primary account to avoid sharing their main address with marketers.
- Spam trap. The email doesn’t belong to a legitimate consumer and is being used to test your email hygiene practices. Sometimes, a formerly active email is converted to a spam trap. This is one of the reasons you should regularly review your subscription list and have a sunset policy.
- Toxic domain. It’s not just sender domains that can get a bad reputation. Toxic domains are known for distributing spam, creating bot emails, or engaging in other destructive behavior. You don’t want emails from these domains on your mailing lists.
How can you tell what services you’re getting?
Each provider is different, so you’ll have to ask.
A free or low-fee service will likely offer some of the basic validation checks. However, a free service may not offer the full range of validation and verification checks or limit how many emails you can check.
A verification service is more likely to offer a range of validation, verification, and email list hygiene services for different pricing tiers.
The one you choose will depend on your goals and your budget. If you engage in good list hygiene practices, you may not need in-depth verification for your lists.
Now, let’s dig deeper into the facts about email validation.
What’s going on behind the scenes when you ask for an email to be validated?
The different stages of the email validation process
As you’ve probably figured out, email validation isn’t just one check. Instead, it’s a series of tests, each one moving the email closer to passing its validation check.
Below, I listed some of the most common types of validation checks. Keep in mind that not every validation service or software program will run every check–and they may not need to.
Syntax
At the most basic, an invalid email isn’t formatted correctly. For this reason, nearly every email check begins with a syntax check, sometimes referred to as a regex validation.
A syntax check looks for the presence of elements required by the syntax criteria presented in the Internet Society of the Internet Engineering Task Force’s Request for Comments (RFC) at section 5322.
This automated check will also look for elements the RFC prohibits.
For instance, every email must have a local address or username that precedes the @ symbol. However, this local address cannot exceed 64 characters. It also cannot begin or end with a dot or include two consecutive dots.
Domain names are limited to 255 characters maximum and cannot include two consecutive hyphens. The domain portion of the address also cannot end with a dot.
And, of course, every email address must have an @ between the local address and the domain.
Domain check
Subscribers or bots can enter fake domains, and old domains can expire. A quick check by your verification service can confirm that the domain associated with a submitted email address exists and is operational.
MX records
This test confirms that the email’s receiving domain can receive emails. To do this, the validation service checks to see if the domain has any mail exchange (MX) servers. If there are no MX servers associated with a domain, it may be up to something, but it’s not accepting emails!
This example MX record was created by Cloudflare. It identifies the mail servers and their routing priority.

SMTP server check
Your email’s going to have to pass through the recipient’s SMTP server to get to them. Are the SMTP servers revealed by the MX check operational? This test will find out.
SMTP mailbox
After you’ve verified that the domain is legitimate and the server works, you still need to investigate the actual email account.
Does it exist on that server?
Validation programs use the HELO command to ask or “ping” the email box to find out without sending an email to the mailbox (and risking a bounce).
When using this protocol, the validator can determine if there is an active mailbox associated with the email address in its query.
The results below from a test using the Deep Email Validator app show an email that passed 4 out of 5 checks. But it is invalid because it failed the SMTP ping.
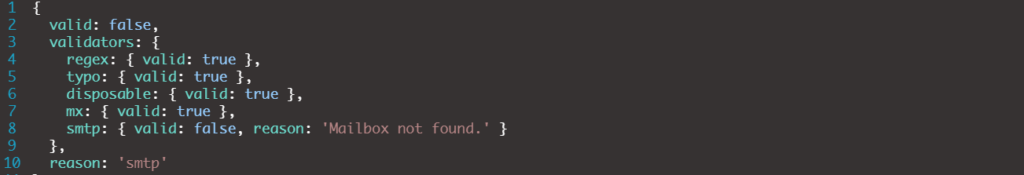
Caution: The mailbox check doesn’t work if a domain’s SMTP server is set to “accept all.” This setting accepts any incoming email addressed to the domain, whether it is valid or not. Every ping gets a yes.
The above tests are among the most basic and will tell you:
- Whether the entry is technically valid.
- Whether the domain can accept emails.
- Whether the email exists on the designated server.
Performing these first-line validity tests can help you avoid many emails that might cost you a bounce, but not all.
There are other checks that your validation service can perform that can further reduce your chances of email bounce backs, improve your list’s quality, and protect your sender reputation.
Those test may include the following:
Common typos
This check requires your validation service to make some assumptions about user intent.
A service that screens for common typos will use an automated program that replaces entries like “gooogle.com” with “google.com” to fix a wrong address.
Extra dots accidentally entered at the beginning or end of an email might be a candidate for this type of correction as well.
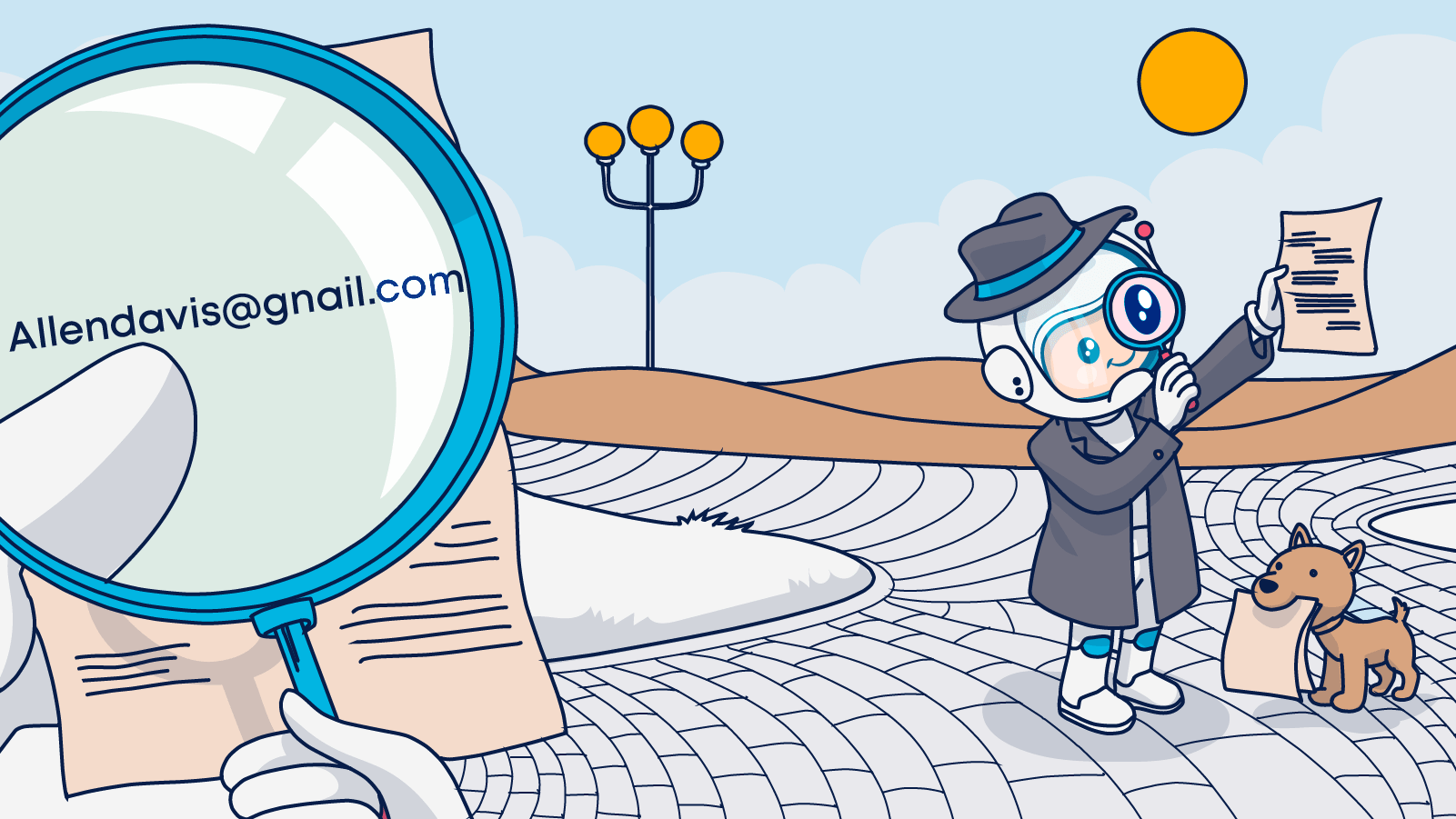
This validity report generated by Email Checker for mailtrap.io shows a typo (“gnail.com”) and the suggested fix. Without the fix, the email will remain listed as “invalid.”
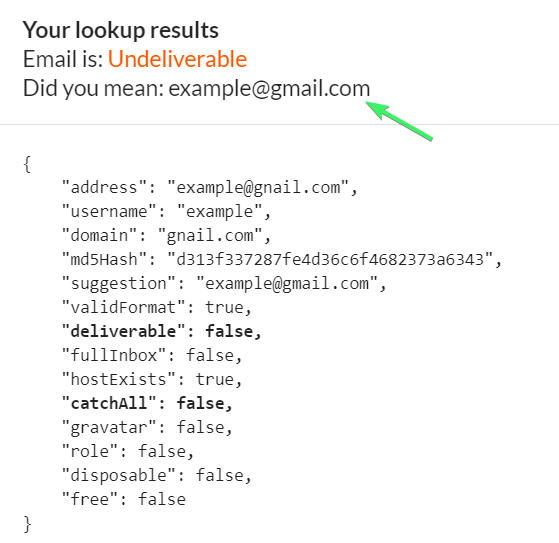
Potential bot addresses
Some bots just don’t get human interactions. So, when they generate their fake bot email addresses, they don’t follow standard human conventions–like using words that make sense.
This would be similar to a media fact-checker calling out a date or name because it simply doesn’t make sense (unless you’re Elon Musk naming your first child).
One example is the email verification service Hunter.io that checks for what it calls “gibberish email addresses” to identify bots.
Catch-all policies
Your verification service can check to determine if an SMTP server or domain has an accept-all protocol in place that prevents you from getting precise results when you ping the server for an individual address.
Undesirable domains
An undesirable domain is one that is unlikely to yield a quality lead or is downright dangerous.
This category may include:
- Temporary or disposable mailbox providers.
- Spam traps.
- Toxic domains.
Validation providers often maintain databases of different suspect domains, making it easy to spot them when checking new emails.
Depending on the types of subscribers you want to attract, you may decide to add free mailbox providers to your list of undesirables as well. Many validation providers offer this option.
What should you look for in an email validation service?
There are plenty of different validation services from which to choose. When making your choice, keep your goals and your budget in mind.
Remember to find out what services each provider offers and whether you can choose different service levels.
In addition to making sure they offer what you want, also investigate:
- Whether the service can handle the volume of emails you need to process.
- How quickly bulk validations are performed. Will your list be processed in a few hours, or will it take a few days to get a return report?
- Is the real-time validation reliable and seamless for customers?
- Is the service’s software compatible with your sign-up forms?
- How integrations are handled. Will you be able to efficiently conduct bulk email checks and sync the results with your lists?
- How accurate are the validation service’s results? What tests do they conduct to assure accuracy?
- What do other customers say about the company’s performance? Do they receive the support they need?
Finally, choose a fact-checker you trust–your reputation depends on it.
What comes after email validation?
Like the fact-checkers who inspected each Time Magazine article before it went to press, email validation keeps you from doing something that might damage your reputation.
But, validation is just one part of the process. There’s more you can do to maintain a clean subscriber list.
First, capture your emails the right way
Never scrape the web for emails or use a purchased list. Addresses obtained this way are likely to have more than a fair share of spam traps and other types of non-sender-reputation-friendly email addresses.
Use sign-up forms using the strategies we describe in our article and other methods that acquire the subscriber’s consent to expand your email list.
Here’s some inspiration to get you started:
Second, double opt-in to double-check your subscribers’ intent
Double opt-ins are a way for you to validate your subscribers’ email addresses and confirm their interest in your brand. Unlike an SMTP ping, a double opt-in requires you to send an email to the subscriber asking them to confirm their address.
That means you may get a bounce if the email is invalid.
However, you can significantly cut your bounce risk if you use the double opt-in method after performing your other validation checks.
Next, make sure you are giving all your subscribers options
Your email recipients should quickly locate the link to your preference center and unsubscribe button in every email.
This email from one of our customers, Kayak, gives subscribers a straightforward way to manage their preferences or unsubscribe.
Why make it easy?
People are more likely to engage when they can do it on their terms. Someone who was planning to unsubscribe because they received too many emails may decide to stick around if your preference center gives them the option to lower the volume.
If a customer does want to unsubscribe, there’s no benefit in preventing it. All you accomplish by making things complicated is a spam complaint.
Also, develop a sunset policy to remove inactive subscribers proactively
Unengaged subscribers, at best, are non-profitable. At worst, these inactive emails may become spam traps. It’s better to remove them from your list than to take that risk.
To implement a sunset policy using Ongage:
- Create a segment for your least engaged subscribers.
- Then, use a re-engagement campaign to check on their interest one last time.
- If they don’t respond, place them on your suppression list. The sun has set on that relationship.
Here’s an example of what your sunset setting might look like using Ongage:
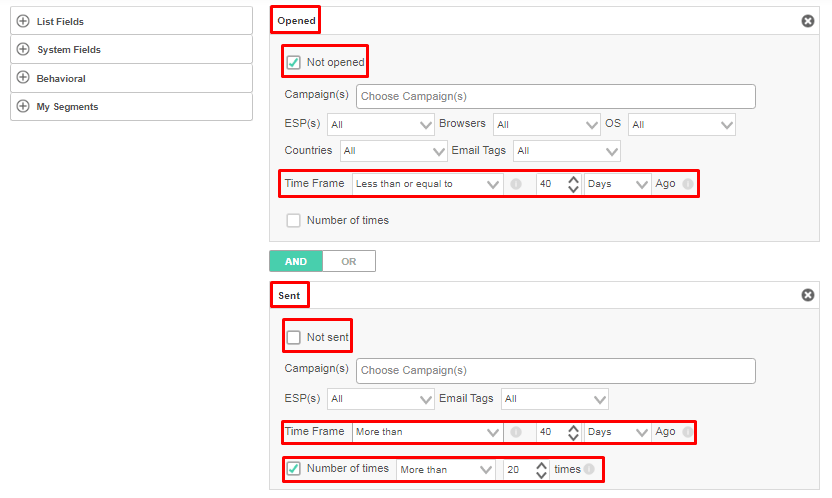
Keeping your email lists clear of decaying data helps you stay ahead of spam traps and improves your engagement metrics. Now that’s good news!
Good email validation protects your sender reputation and get your message to the right audience
Email validation is a fast and effective way to ensure that the addresses are accurate, valid, and won’t lead to a bounce.
Once you know your subscribers are real, you can then send them engaging, value-adding content that builds a strong relationship.
How do you build relationships that convert subscribers into loyal customers?
One of the first opportunities you have to connect with your new subscriber may be through your transactional emails. This email could be a double opt-in message, confirmation of their sign-up, or a recent purchase.
Don’t miss this chance to make a great first impression! Follow the tips in our updated guide above. It has the facts and advice you need to take you every step of the way.
In addition, don’t miss the opportunities to build relationships that convert subscribers into loyal customers?
Try the tips in our email personalization post; It’s full of fascinating facts and advice that will help you get to know your customers and deliver a premium experience with every email you send once email validation is done.